|
|
|
  

|
|
|
|
|
AP Government Review Sheet and AP Gov Cram Packet AP Gov review sheet, flashcards, notes, and study guide for the AP® Government and Politics test. FORMAT OF NEW AP US GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS EXAM Key Terms To Know (click the links)
Legislative Veto, Committee and Chairs, Standing Committee, Ways and Means Committee, Rules Committee, Appropriations Committee, Bill, Filibuster, Rider, Logrolling, Pork-Barrel Legislation, Reapportionment, Gerrymandering, Initiative, Referendum, and Recall, Line-Item Veto, Pocket Veto, Resolutions of Congress, Open and Closed Primary, Nominating Convention, Electoral College, Plurality and Winner-Take-All, Executive Order, War Powers Act, Cabinet, White House Staff, EOP, Independent Regulatory Agencies, Federal Reserve Board, Legislative Oversight, Advice and Consent, Executive Privilege, Presidential Approval Rate, Presidential Succession, Lame Duck, Original and Appellate Jurisdiction, Judicial Review, Writ of Certiorari, Original Intent and Living Constitution, Judicial Activism and Judicial Restraint, Stare Decisis, Court Packing Scheme, Plea Bargain, Class Action Suit, Amicus Curiae, Bureaucracy, Merit System, Bureaucratic Discretion, Casework, Monetary and Fiscal Policy, National Debt and Sequester, Keynesian Economics, Supply Side Economics, Iron Triangle, Issue Network, Jim Crow, De Jure and De Facto Segregation, Civil Disobedience, Little Rock 9, Naturalization, Establishment Clause and Free Exercise Clause, Wall of Separation, Selective Incorporation, Exclusionary Rule, Affirmative Action, Equal Rights Amendment
Foundational Documents
There are 9 Foundational Documents that YOU NEED TO KNOW. These are
explained within the pages of No Bull Review. They include:
2.
Brutus No. 1
3. The Declaration of Independence
4. The Articles of Confederation
5. The Constitution of the United
States (including the Bill of Rights
and subsequent Amendments)
7.
Letter from a Birmingham Jail
Key Questions (click the links)
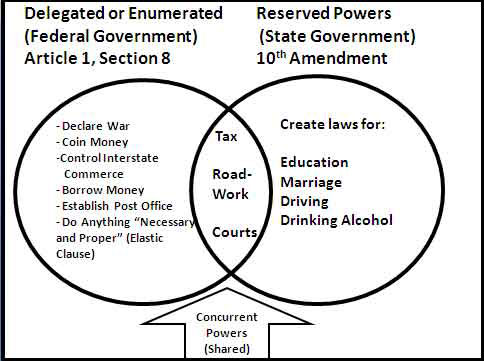
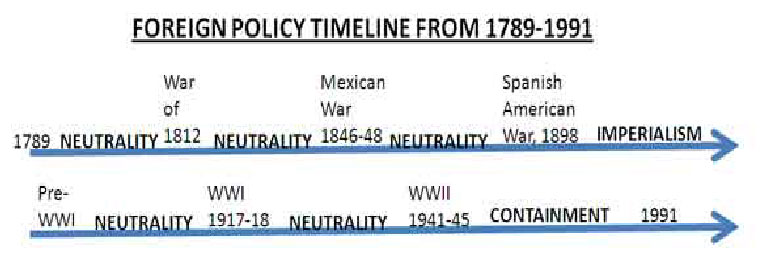
What do the three branches of government do?
What are the main powers of each branch?
What are the qualifications to hold major office?
What types of federal grants should I know?
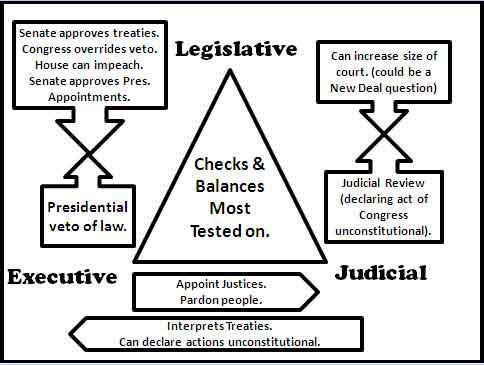
What are the most important checks and balances to know?
What ideologies do I need to know? What’s a liberal? What’s a
conservative?
How does the US compare to other nations in terms of voter
turnout? What obstacles do voters face?
What types of ballots should I know?
What do I need to know about the history of political parties?
How might candidates at the state level stray from the
national party platform?
What has happened to the number of interest groups over the
last 60 years?
What are some specific special interest groups to
know, and what do they support?
What forms of media are there?
How does the media affect public policy?
What is the relationship between the President and the media?
What are the powers of Congress?
What are some major differences between the House and the
Senate?
What standing committees should I know about?
How does the President win an Election?
How does the Supreme Court operate? …
What other tidbits are relevant to know?
How might special interests affect who is appointed to the
Supreme Court?
Since the early twentieth century, what has happened to the
size of the bureaucracy?
What types of jobs make up the bureaucracy?
How can the bureaucracy be checked?
How is the federal budget created?
Amendments Lesson and Bill of Rights Song
Bill of Rights Amendments to Know
1st
– Freedoms of speech, press, religion, assembly, and right to
petition the government.
2nd
– Right to bear arms.
4th
– Freedom from unreasonable searches and seizures.
5th
– Due process rights (right to fair justice, and freedoms from
self incrimination). Also, one cannot be tried twice for the
same crime. This is a freedom from “double-jeopardy.”
6th
– Right to a fair trial and attorney. 10th – Division of powers between the states and federal government (called federalism).
Civil War/Reconstruction Amendments
13th Amendment – Abolition of Slavery
14th Amendment – Equality and Due Process Clause
15th Amendment – Universal Male Suffrage Progressive Era Amendments
16th Amendment – Graduated Income Tax
17th Amendment – Direct Election of Senators
19th Amendment – Women’s Suffrage These Could Come Up As Well
22nd Amendment – Two Term Limit for Presidents
25th Amendment – Clarified succession of the President, and
vacancy of Vice President’s office.
26th Amendment – Lowered the voting age to 18 in 1971, as
Vietnam War soldiers were not old enough to vote.
Checks and Balances Song
FORMAT OF NEW AP US GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS EXAM COURT CASES - WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW!
AP Gov Required Supreme Court Cases
Court Cases You Should Know (**14 are Required)..
Federal and State Power **Marbury v. Madison, 1803 - First use of judicial review. **McCulloch v. Maryland, 1819 - Maryland could not tax the Bank of the United States because of federal supremacy, and the right of the national government to charter a bank.
**US
v. Lopez,
1995
– Possession of a gun in a school zone does not violate the Commerce
Clause.
Civil Rights
First Amendment (School Cases Listed in Own Category)
**Schenck v. US,
1919 - Said that free speech was not absolute. One can’t utter
something that creates a “clear and present danger,” as
someone can’t shout “FIRE!” in a crowded theater.
New York Times Co. v. Sullivan,
1964
- Protected freedom of the press. Libel, or printing false
statements against public officials, was only punishable if there
was knowledge of the mistakes written, and intent to harm. Without
such malice, damages could not be awarded.
Fourteenth Amendment
Obergefell
v.
Hodges,
2015 - The Fourteenth
Amendment prevents states from refusing to license and recognize
same-sex marriages.
Other Constitutional Issues
**Baker v. Carr,
1962 – The Supreme Court ruled that the federal courts could
hear cases and force states to redraw where the districts are. Wesberry v. Sanders, 1964 - Districts had to be of similar populations, adhering to the principle of “one person, one vote.” **Shaw v. Reno, 1993 - Districts can’t be shaped to benefit a particular race. Buckley v. Valeo, 1976 – Campaign contributions are a form of free speech protected by the First Amendment. Gregg v. Georgia, 1976 - Chief Justice Warren Burger’s Court decided that the death penalty does not automatically violate the Eighth (freedom from cruel and unusual punishment) and Fourteenth Amendments.
**McDonald
v.
Chicago,
2010
- The Second Amendment’s right to bear arms applies to the states.
Griswold v. Connecticut,
1965 - A Connecticut law making it illegal for married people
to obtain contraceptives (birth control) was declared
unconstitutional. The right to a married couple’s privacy was
protected. Regents of the University of California v. Bakke – Race can be considered in the university admissions process, but distinct racial quotas are illegal.
United States v. Nixon,
1974 - President Richard Nixon was not protected by executive
privilege, and had to hand over tape-recordings. Nixon remains
the only President to resign the office.
Bush v. Gore,
2000 - Ended Al Gore’s Campaign’s sponsoring of hand-counting
ballots in Florida’s Presidential Election.
Cases Involving a School
(for Brown v.
Board, see above) **Tinker
v. Des Moines , 1969 - A student
wanted to protest the Vietnam War, so he and some friends wore
a black armband. They were suspended for making such a
political statement. The Supreme Court ruled that clothing is
an extension of free speech (First Amendment), and the
students should not have been suspended. **Engel v. Vitale, 1962 - The Supreme Court ruled that official school-sponsored prayer is a violation of the free exercise clause of the First Amendment. **Wisconsin v. Yoder, 1972 – Children cannot be forced to attend schools if it violates their religious practices.
Lemon v. Kurtzman, 1971 –The decision created the
“Lemon Test” where a government’s laws had to be secular,
can’t have the primary effect of advancing or inhibiting
religion, and can’t have entanglements with religion.
Everson v. Board of Education, 1947 – The Supreme Court decided that the
busing was constitutional, as the benefits to the students was
the main purpose of the law, and not the helping of a
religious institution.
Important Acts to Know
US Gov and Politics in 14 Minutes!!!!
US Review in 18 Minutes! Brace yourself.
Reviews of all Three Branches!!!
Click here for the US History Review Song!
LINKS TO LATEST EDITIONS OF NO BULL REVIEW ...
AP US History AP World History Global 2 Regents US History Regents
Toiletrivia: Bathroom Trivia Books in Print and Kindle
AP ® is a trademark registered by the College Board, which is not
affiliated with, and does not endorse, this product.
|
|



 S
S